基于 Python3。多多练习。
Python 常用库的示意图。(提供 Xmind 格式下载 )
Python 标准库 。
Awesome Python 。
kite 智能编程工具,AI-Powered Python Copilot,Kite_blog (暂时不太好用)Sublime Text 3 绝对神器 ,sublime text 3 插件推荐? ,Emmet 文档 ,HTML/CSS 速写神器:Emmet | bubkoo ,前端开发必备!Emmet 使用手册_Emmet 教程_w3cplus ,实用的 sublime 插件集合 – sublime 推荐必备插件
入门 Python 数据分析最好的实战项目(一) ,(二)
安装格式 :(Python 安装包工具有 easy_install、pip、setuptools、distribute、conda 等)
1 2 3 4 //以pip为例,在cmd命令行输入 pip install 安装库名称 //安装 pip install -U 库名称 //更新 pip uninstall 库名称 //卸载
(如果直接使用 Anaconda 会被自动安装 )
调用格式 :(More )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #在.py文件中输入,类似C语言的#include<…> import sys #引入1个库 import sys as ss #引入的同时取一个别名 import matplotlib.pyplot #引入子库 import os, sys, time #同时引入多个库 from os import path, walk, unlink #从……导入……功能 from os import * #导入库中所有内容
import 库是有时间和空间成本 的,斟酌而行。
当使用的库数量众多时,考虑环境管理 。
在线使用 python:(More )
自动格式转换:IPython and Jupyter Notebooks: Automatically Export .py and .html
标准模板库(Standard Template Library),引用自 C++。收录内置库和标准功能库。
1 2 3 import sys from sys import stdin, stdout # 输入输出重定向 # n = int(stdin.readline())
参考资料:
python 之 sys 模块详解
sys.argv: 实现从程序外部向程序传递参数 。sys.exit([arg]): 程序中间的退出,arg=0 为正常退出。sys.executable: 程序执行器路径 (比如 C:/Anaconda/python.exe)sys.getdefaultencoding(): 获取系统当前编码 ,一般默认为ascii。sys.setdefaultencoding(): 设置系统默认编码
执行 dir(sys)时不会看到这个方法,在解释器中执行不通过
设置UTF-8 :可以先执行reload(sys),在执行 setdefaultencoding('utf8'),此时将系统默认编码设置为 utf8。(见设置系统默认编码 )
sys.getfilesystemencoding(): 获取文件系统使用编码方式,Windows 下返回’mbcs’,mac 下返回’utf-8’.sys.path: 获取指定模块搜索路径的字符串集合,可以将写好的模块放在得到的某个路径下,就可以在程序中 import 时正确找到。dir()类似,可以返回当前 namespace 中的名称列表。sys.modules: 返回已经import的库的名称列表sys.platform: 获取当前系统平台。sys.stdin,sys.stdout,sys.stderr: stdin , stdout , 以及 stderr 变量包含与标准 I/O 流对应的流对象. 如果需要更好地控制输出, 而 print 不能满足你的要求, 它们就是你所需要的. 你也可以替换它们, 这时候你就可以重定向输出和输入到其它设备 (device), 或者以非标准的方式处理它们
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/001478651770626de401ff1c0d94f379774cabd842222ff000
控制文件读写前后的修饰操作。
参考资料:
http://www.runoob.com/python/os-file-methods.html
os 模块提供了非常丰富的方法用来处理文件和目录。详见参考网址。
os.system(instruction)
例子:(保存animation)
1 2 os.system("ffmpeg -i C:\\my_path\\animation.mp4 C:\\my_path\\animation.gif") # \\ allows to bypass any ascii issue because for example in python "\a" means "\x07" and "\\a" means "\a"
例 2:(检测库是否安装,否则自动安装库 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 try: import requests except : import os os.system('pip install requests') import requests
https://github.com/giampaolo/psutil
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/001511052957192bb91a56a2339485c8a8c79812b400d49000
在 Python 中获取系统信息。
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/001432712108300322c61f256c74803b43bfd65c6f8d0d0000
多版本管理。Anaconda 的activate可以实现类似功能。
https://docs.python.org/3/library/struct.html#format-characters
将数据转化为字节。
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/0014319556588648dd1fb0047a34d0c945ee33e8f4c90cc000
Python 的 hashlib 提供了常见的摘要算法,如 MD5,SHA1 等等。
哈希的本质是在维度上的嵌入,而降维算法则是维的嵌入。
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/0015108777177966ef0f4f8510a41b3b8c48cdcf7047b2d000
为了防止黑客通过彩虹表 根据哈希值反推原始口令,在计算哈希的时候,不能仅针对原始输入计算,需要增加一个salt来使得相同的输入也能得到不同的哈希,这样,大大增加了黑客破解的难度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 from collections import namedtuple #指向tuple的字典 from collections import deque #双端队列 from collections import defaultdict #不命中特殊返回的字典 from collections import OrderedDict #有序字典 from collections import ChainMap #二维字典 from collections import Counter #相当于multiset
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/001431953239820157155d21c494e5786fce303f3018c86000
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/00143200162233153835cfdd1a541a18ddc15059e3ddeec000
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/001431954588961d6b6f51000ca4279a3415ce14ed9d709000
Base64 是一种用 64 个字符来表示任意二进制数据的方法。
1 2 3 4 import chardet data = '离离原上草,一岁一枯荣'.encode('gbk') chardet.detect(data) # {'encoding': 'GB2312', 'confidence': 0.7407407407407407, 'language': 'Chinese'}
自动检测编码。
参考资料:
http://www.runoob.com/python/python-date-time.html
时间处理 包含多个模块:
time.time(): 时间戳。(自从 1970 年 1 月 1 日午夜)
time.localtime(time.time()): 将时间戳转化为本地时间
time.asctime( time.localtime(time.time()) ): 格式化
random
http://www.runoob.com/python/func-number-random.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import random print( random.randint(1,10) ) # 产生 1 到 10 的一个整数型随机数 print( random.random() ) # 产生 0 到 1 之间的随机浮点数 print( random.uniform(1.1,5.4) ) # 产生 1.1 到 5.4 之间的随机浮点数,区间可以不是整数 print( random.choice('tomorrow') ) # 从序列中随机选取一个元素 print( random.randrange(1,100,2) ) # 生成从1到100的间隔为2的随机整数 a=[1,3,5,6,7] # 将序列a中的元素顺序打乱 random.shuffle(a) print(a)
参考资料:
re — 正则表达式操作— Python 3.7.2 文档
re — Regular expression operations — Python 3.7.2 documentation
Python 正则表达式 | 菜鸟教程
Python 正则表达式指南
正则表达式的大致匹配过程是:依次拿出表达式和文本中的字符比较,如果每一个字符都能匹配,则匹配成功;一旦有匹配不成功的字符则匹配失败。如果表达式中有量词或边界,这个过程会稍微有一些不同,但也是很好理解的,看下图中的示例以及自己多使用几次就能明白。
re就是模式匹配 工具。
1 2 import math import cmath #复数运算
参考资料:
Python math 模块与 cmath 模块 | 菜鸟教程
math — Mathematical functions — Python 3.7.2 documentation
cmath — Mathematical functions for complex numbers — Python 3.7.2 …
1 from urllib import request, parse
参考资料:
urllib — URL handling modules — Python 3.7.2 documentation
urllib - 廖雪峰的官方网站
urllib 提供了一系列用于操作 URL 的功能。
快速上手— Requests 2.18.1 文档 - Python Requests
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/0015109021115795adfc5c8629f4f98985063b5a7e3ff87000
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import requests r = requests.get('https://www.google.com/') # 博客首页 print(r.status_code) #状态码:200时为正常 print(r.text) #内容 print(r.encoding) #编码 print(r.content) #获得内容的bytes对象 print(r.headers) #响应头 # print(r.cookies['ts']) #获取指定的Cookie # 带参数的URL r = requests.get('https://www.douban.com/search', params={'q': 'python', 'cat': '1001'}) print(r.url) # 实际请求的URL:'https://www.douban.com/search?q=python&cat=1001' # 超时控制 requests.get('https://www.google.com/', timeout=0.001)= #其它操作 r = requests.post('https://accounts.douban.com/login', data={'form_email': 'abc@example.com', 'form_password': '123456'}) #发送数据
1 2 from html.parser import HTMLParser from html.entities import name2codepoint
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958f449949df42a6d3a2e542c000/0014320023122880232500da9dc4a4486ad00426f081c15000
1 2 3 from PIL import Image from PIL import Image, ImageFilter from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont, ImageFilter
Pillow — Pillow (PIL Fork) 5.4.1 documentation
Pillow - 廖雪峰的官方网站
PIL:Python Imaging Library,已经是 Python 平台事实上的图像处理标准库了。PIL 功能非常强大,但 API 却非常简单易用。由于 PIL 仅支持到 Python 2.7,加上年久失修,于是一群志愿者在 PIL 的基础上创建了兼容的版本,名字叫 Pillow ,支持最新 Python 3.x,又加入了许多新特性,因此,我们可以直接安装使用 Pillow。
Python 图像处理(Pillow/PIL)入门
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 from PIL import Image # 打开一个jpg图像文件,注意是当前路径: im = Image.open('test.jpg') # 获得图像尺寸: w, h = im.size print('Original image size: %sx%s' % (w, h)) # 缩放到50%: im.thumbnail((w//2, h//2)) print('Resize image to: %sx%s' % (w//2, h//2)) # 把缩放后的图像用jpeg格式保存: im.save('thumbnail.jpg', 'jpeg') #-------------------------模糊效果----------------------------------- from PIL import Image, ImageFilter # 打开一个jpg图像文件,注意是当前路径: im = Image.open('test.jpg') # 应用模糊滤镜: im2 = im.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR) im2.save('blur.jpg', 'jpeg') #---------------------生成字母验证码图片------------------------------- from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont, ImageFilter import random # 随机字母: def rndChar(): return chr(random.randint(65, 90)) # 随机颜色1: def rndColor(): return (random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255)) # 随机颜色2: def rndColor2(): return (random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127)) # 240 x 60: width = 60 * 4 height = 60 image = Image.new('RGB', (width, height), (255, 255, 255)) # 创建Font对象: font = ImageFont.truetype('Arial.ttf', 36) # 创建Draw对象: draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image) # 填充每个像素: for x in range(width): for y in range(height): draw.point((x, y), fill=rndColor()) # 输出文字: for t in range(4): draw.text((60 * t + 10, 10), rndChar(), font=font, fill=rndColor2()) # 模糊: image = image.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR) image.save('code.jpg', 'jpeg')
Home - tqdm documentation
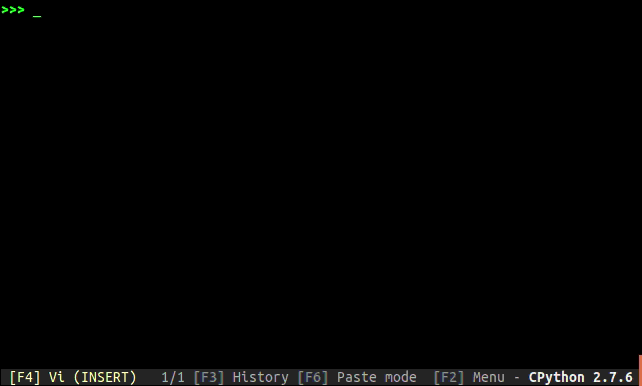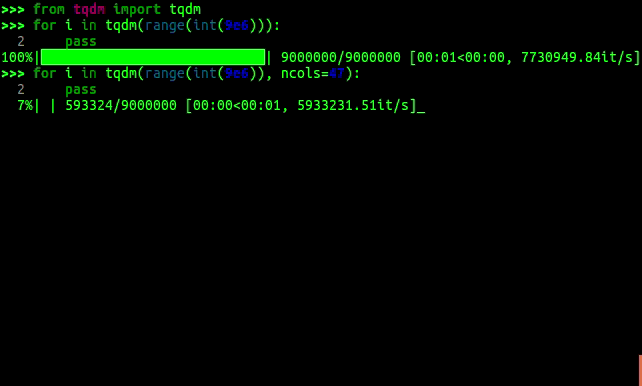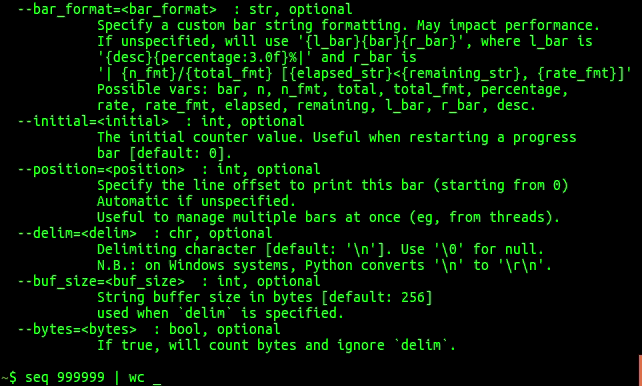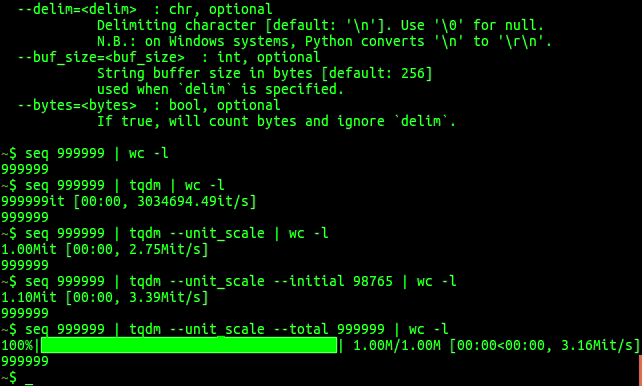
【python】用 tqdm 模块实现进度条显示
从 Python 第三方进度条库 tqdm 谈起
python tqdm 模块分析 · LoRexxar’s Blog
python 模块之——tqdm(进度条)
tqdm不属于标准库,但它的功能很标准。主要用于显示进度条 。
参考资料:
Numpy 中文文档 。(More )
如何系统地学习 Python 中 matplotlib, numpy, scipy, pandas?
中文 Python 笔记
Numpy 教程
jupyter notebook 导入 python code
jupyter code 和 markdown 转换 (含常用快捷键)
100 numpy exercises
Numpy 的应用范围 :
机器学习模型 :
图像处理和计算机图形学 :
数学任务 :
NumPy 的主要对象是同类型的多维数组 。它是一张表,所有元素(通常是数字)的类型都相同,并通过正整数元组索引。在 NumPy 中,维度称为轴 (axis)。轴的数目为 rank。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import numpy as np #引入 print("Numpy定义数组....................") #Numpy定义数组 my_array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) #传入参数必须是一个数字列表 print("打印方式....................") #打印方式 print(my_array) #打印数组:[1 2 3 4 5] print(my_array.shape) #输出数组的形状:(5,) print(my_array[0]) #打印数组的某个元素:1 print(my_array[1]) #:2 print("修改数组元素....................") #修改数组元素 my_array[0] = -1 print(my_array) #:[-1 2 3 4 5] print("快速创建向量....................") #快速创建向量 my_new_array = np.zeros((5)) #类似的,np.ones np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int16 ) #指定数据类型的全1向量 np.arange( 10, 30, 5 ) #均匀分布 in [10, 30] 指定间距为5 b = np.arange(6) # :[0 1 2 3 4 5] x = np.linspace( 0, 2, 9 ) # 均匀分布(指定元素数) 9 numbers int [0, 2] f = np.sin(x) #可以很方便地为调用pyplot画图做准备 my_random_array = np.random.random((2, 3)) #随机向量 print("二维向量....................") #二维向量 my_2d_array = np.zeros((2, 3)) my_array = np.array([[4, 5], [6, 1]]) #自行设置元素 print(my_array),print(my_array[0][1]) #:[[4 5] [6 1]] and 5(0行1列) my_array_column_2 = my_array[:, 1] #提取子矩阵(第1列元素) print("张量....................") #张量 my_array = np.zeros(2) #1阶张量-矢量 print(my_array) my_array = np.zeros((2, 3)) #2阶张量-矩阵 print(my_array) my_array = np.zeros((2, 3, 4)) #3阶张量 print(my_array) my_array = np.zeros((2, 3, 4, 5)) #4阶张量 print(my_array) #......直至n阶张量
NumPy 的数组类被称为 ndarray 。别名为 array。 请注意,numpy.array 与标准 Python 库类 array.array 不同,后者仅处理一维数组并提供较少的功能。 ndarray 对象则提供更关键的属性:
ndarray.ndim :数组的轴(维度)的个数。在 Python 世界中,维度的数量被称为 rank。ndarray.shape :数组的维度(就是形状 )。这是一个整数的元组,表示每个维度中数组的大小。对于有 n 行和 m 列的矩阵,shape 将是 (n,m)。因此,shape元组的长度就是 rank 或维度的个数 ndim。ndarray.size :数组元素的总数。这等于 shape 的元素的乘积。ndarray.dtype :一个描述数组中元素类型 的对象。可以使用标准的 Python 类型创建或指定 dtype。另外 NumPy 提供它自己的类型。例如 numpy.int32、numpy.int16 和 numpy.float64。ndarray.itemsize :数组中每个元素的字节大小。例如,元素为 float64 类型的数组的 itemsize 为 8(=64/8),而 complex32 类型的数组的 itemsize 为 4(=32/8)。它等于 ndarray.dtype.itemsize 。ndarray.data :该缓冲区包含数组的实际元素。通常,我们不需要使用此属性,因为我们将使用索引访问数组中的元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 import numpy as np #引入 #矩阵运算 a = np.array([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]]) #2X2矩阵 b = np.array([[5.0, 6.0], [7.0, 8.0]]) #同型矩阵 sum = a + b #加 a += 1 #自加 difference = a - b #减 product = a * b #逐元素乘 a *= 2 #自乘 quotient = a / b #逐元素除 matrix_product = a.dot(b) #矩阵乘法 #or matrix_product = np.dot(a, b) #矩阵变形 v = np.transpose(np.array([[2,1,3]])) #矩阵转置 b = np.arange(12).reshape(4,3) #返回整形后的矩阵 c = np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4) b.resize(2,6) #修改b数组本身 #广播(矩阵的自动匹配) a = np.array([1.0, 2.0, 3.0]) b = 2.0 a * b #广播,b被自动展成[2.0, 2.0, 2.0] #通用函数 #NumPy提供了常见的数学函数,如sin,cos和exp。 np.exp(np.arange(3)) a = np.ones((3,4)) b = np.ones((3,4)) np.add(a, b) b = np.arange(12).reshape(3,4) b.sum(axis=0) #指定轴向的操作,这是在0号维度(竖着)上进行加法压缩 b.min(axis=1) # min of each row ,返回值仍然是一个行向量 b.cumsum(axis=1) # cumulative sum along each row data = 10*np.random.random((3,4)) a = np.around(data) #四舍五入 a = np.floor(data) #上取整 a = np.ceil(data) #下取整 a = np.where(data>0.5,data,0) #逻辑过滤 #解线性方程组 A = np.array([[2,1,-2],[3,0,1],[1,1,-1]]) b = np.transpose(np.array([[-3,5,-2]])) #x = np.linalg.solve(A,b) #线性回归。原理是正规方程,这个变换下不用显性求逆 X = np.random.random((3,4)) y = np.transpose(np.array([[3,2,5]])) Xt = np.transpose(X) XtX = np.dot(Xt,X) Xty = np.dot(Xt,y) beta = np.linalg.solve(XtX,Xty) #索引、切片和迭代 a = np.arange(10)**3 #**是指数符号,相当于^ a[2:5] #里面的数字就是索引。区间就是切片:array([ 8, 27, 64]) a[:6:2] = -1000 #迭代赋值,2为步长,区间[0,6)。相当于a[0:6:2] # 注——对于:冒号语法,默认的区间都是前闭后开![a,b) a[ : :-1] # reversed a for element in a.flat: print(element) #flat属性是数组中所有元素的迭代器
参考资料:
Pandas 中文文档
Pandas Cheat Sheet - Dataquest
Pandas-Cheat PDF ),Pandas 速查手册中文版 - 知乎
Github-Pandas
DataFrame——数据选取与筛选
Main Features
Here are just a few of the things that pandas does well:
Easy handling of missing data NaN) in floating point as well as non-floating point data
Size mutability: columns can be inserted and deleted
Automatic and explicit data alignment Series, DataFrame, etc. automatically align the data for you in computations
Powerful, flexible group by
Make it easy to convert
Intelligent label-based slicing fancy indexing subsetting
Intuitive merging joining
Flexible reshaping pivoting
Hierarchical Robust IO tools for loading data from flat files Excel files databases HDF5 format
Time series
总结:数据预处理 ,数据流 / IO 管理,鲁棒群操作 ,时间序列处理 等。
pd.read_csv(filename)pd.read_table(filename) | From a delimited text file (like TSV)pd.read_excel(filename) | From an Excel filepd.read_sql(query, connection_object) | Read from a SQL table/databasepd.read_json(json_string) | Read from a JSON formatted string, URL or file.pd.read_html(url) | Parses an html URL, string or file and extracts tables to a list of dataframespd.read_clipboard() | Takes the contents of your clipboard and passes it to read_table()pd.DataFrame(dict) | From a dict, keys for columns names, values for data as lists
df.to_csv(filename,index=False)index=False不额外保存行号)df.to_excel(filename) | Write to an Excel filedf.to_sql(table_name, connection_object) | Write to a SQL tabledf.to_json(filename)
Useful for testing code segements
pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(20,5)) | 5 columns and 20 rows of random floatspd.Series(my_list) | Create a series from an iterable my_listdf.index = pd.date_range('1900/1/30', periods=df.shape[0]) | Add a date index
df.head(n)df.tail(n) | Last n rows of the DataFramedf.shape | Number of rows and columnsdf.info() | Index, Datatype and Memory informationdf.describe() | Summary statistics for numerical columnss.value_counts(dropna=False) | View unique values and countsdf.apply(pd.Series.value_counts) | Unique values and counts for all columns
These can all be applied to a series as well.
df.describe()df.mean() | Returns the mean of all columnsdf.corr() | Returns the correlation between columns in a DataFramedf.count() | Returns the number of non-null values in each DataFrame columndf.max() | Returns the highest value in each columndf.min() | Returns the lowest value in each columndf.median() | Returns the median of each columndf.std() | Returns the standard deviation of each column
df['column'].value_counts() 统计某一列值的频率,返回一个频率表 df
Count frequency of values in pandas DataFrame column
df[col] | Returns column with label col as Seriesdf[[col1, col2]] | Returns columns as a new DataFrames.iloc[0] | Selection by positions.loc['index_one'] | Selection by indexdf.iloc[0,:]df.iloc[0,0] | First element of first column
df.columns = ['a','b','c']pd.isnull() | Checks for null Values, Returns Boolean Arrraypd.notnull() | Opposite of pd.isnull()python 进行数据处理——pandas 的 drop 函数 - 众荷喧哗 - CSDN 博客 df.drop('name',axis=1)df.drop(columns=['name']))df.dropna() | Drop all rows that contain null valuesdf.dropna(axis=1) | Drop all columns that contain null valuesdf.dropna(axis=1,thresh=n) | Drop all rows have have less than n non null valuesdf.fillna(x)s.fillna(s.mean()) | Replace all null values with the mean (mean can be replaced with almost any function from the statistics section)s.astype(float)s.replace(1,'one') | Replace all values equal to 1 with 'one's.replace([1,3],['one','three']) | Replace all 1 with 'one' and 3 with 'three'df.rename(columns=lambda x: x + 1) | Mass renaming of columnsdf.rename(columns={'old_name': 'new_ name'})传入字典 ,返回修改表头后的 df(需要赋值)df.set_index('column_one') | Change the indexdf.rename(index=lambda x: x + 1) | Mass renaming of index
pandas 如何去掉、过滤数据集中的某些值或者某些行?
df[df[col] > 0.5]col is greater than 0.5df[(df[col] > 0.5) & (df[col] < 0.7)] | Rows where 0.7 > col > 0.5df.sort_values(col1) | Sort values by col1 in ascending orderdf.sort_values(col2,ascending=False) | Sort values by col2 in descending orderdf.sort_values([col1,col2],ascending=[True,False]) | Sort values by col1 in ascending order then col2 in descending orderdf.groupby(col) | Returns a groupby object for values from one columndf.groupby([col1,col2]) | Returns groupby object for values from multiple columnsdf.groupby(col1)[col2] | Returns the mean of the values in col2, grouped by the values in col1 (mean can be replaced with almost any function from the statistics section)df.pivot_table(index=col1,values=[col2,col3],aggfunc=mean) | Create a pivot table that groups by col1 and calculates the mean of col2 and col3df.groupby(col1).agg(np.mean) | Find the average across all columns for every unique col1 groupdf.apply(np.mean) | Apply the function np.mean() across each columndf.apply(np.max,axis=1) | Apply the function np.max() across each row
Pandas 的 Apply 函数——Pandas 中最好用的函数 - 冬之晓 - CSDN 博客
【Python】Pandas 的 apply 函数使用示例 - Alan Lee - CSDN 博客
pandas: create new column from sum of others
df1.append(df2)df1 to the end of df2 (columns should be identical)pd.concat([df1, df2],axis=1) | Add the columns in df1 to the end of df2 (rows should be identical)df1.join(df2,on=col1,how='inner') | SQL-style join the columns in df1 with the columns on df2 where the rows for col have identical values. how can be one of 'left', 'right', 'outer', `’inner’
数据切分:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/24147278/how-do-i-create-test-and-train-samples-from-one-dataframe-with-pandas
Document
pandas 小记:pandas 时间序列分析和处理 Timeseries
Pandas - 时间序列基础 - 简书
用 Python 进行时间序列数据可视化 - 云 + 社区 - 腾讯云
如何用 Python 做舆情时间序列可视化? – Wang Shuyi – Medium
Python 时间序列案例分析实战—奶牛产奶量预测 - kicilove 的小屋 - CSDN …
使用 Python 3 的时间序列可视化指南 - Howtoing 运维教程
python 时间序列分析
1 2 3 4 5 import numpy as np import matplot.pyplot as plt # ------------------------------------------- # 与上两行效果类似。导入 matplotlib 的所有内容(nympy 可以用 np 这个名字来使用) from pylab import *
参考资料:
https://matplotlib.org/
Pyplot tutorial
Matplot 绘图
Matplotlib 教程
pylab 是 matplotlib 面向对象绘图库的一个接口。它的语法和 Matlab 十分相近。也就是说,它主要的绘图命令和 Matlab 对应的命令有相似的参数。(Matlab 和 Octave 语法有几乎一致,所以可以参考这里 )
plot()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt X = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256, endpoint=True) C,S = np.cos(X), np.sin(X) plt.plot(X,C) plt.plot(X,S) plt.show()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 # 导入 matplotlib 的所有内容(nympy 可以用 np 这个名字来使用) from pylab import * # 创建一个 8 * 6 点(point)的图,并设置分辨率为 80 figure(figsize=(8,6), dpi=80) # 创建一个新的 1 * 1 的子图,接下来的图样绘制在其中的第 1 块(也是唯一的一块) subplot(1,1,1) X = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256,endpoint=True) C,S = np.cos(X), np.sin(X) # 绘制余弦曲线,使用蓝色的、连续的、宽度为 1 (像素)、标签为cosine的线条 plot(X, C, color="blue", linewidth=1.0, linestyle="-", label="cosine") # 绘制正弦曲线,使用绿色的、连续的、宽度为 1 (像素)、标签为sine的线条 plot(X, S, color="green", linewidth=1.0, linestyle="-", label="sine") # 标签位置 legend(loc='upper left') # 设置横轴、纵轴的区间范围 xlim(-4.0,4.0) ylim(-1.0,1.0) # 设置横轴、纵轴记号(比如自然坐标,对数坐标) xticks(np.linspace(-4,4,9,endpoint=True)) yticks(np.linspace(-1,1,5,endpoint=True)) # 以分辨率 72 来保存图片 # savefig("exercice_2.png",dpi=72) # 在屏幕上显示 show()
还有给一些特殊点做注释,坐标轴记号调整等功能。详见参考资料 Matplotlib 教程
fill_between()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 256 X = np.linspace(-np.pi,np.pi,n,endpoint=True) Y = np.sin(2*X) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) #调整图框位置和大小 plt.plot (X, Y+1, color='blue', alpha=1.00) plt.fill_between(X, 1, Y+1, color='blue', alpha=.25) #填充颜色 plt.plot (X, Y-1, color='blue', alpha=1.00) plt.fill_between(X, -1, Y-1, (Y-1) > -1, color='blue', alpha=.25) plt.fill_between(X, -1, Y-1, (Y-1) < -1, color='red', alpha=.25) plt.xlim(-np.pi,np.pi), plt.xticks([]) plt.ylim(-2.5,2.5), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/plot_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
bar()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 12 X = np.arange(n) Y1 = (1-X/float(n)) * np.random.uniform(0.5,1.0,n) Y2 = (1-X/float(n)) * np.random.uniform(0.5,1.0,n) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) plt.bar(X, +Y1, facecolor='#9999ff', edgecolor='white') #直方图 plt.bar(X, -Y2, facecolor='#ff9999', edgecolor='white') #添加数值标签 for x,y in zip(X,Y1): plt.text(x+0.4, y+0.05, '%.2f' % y, ha='center', va= 'bottom') for x,y in zip(X,Y2): plt.text(x+0.4, -y-0.05, '%.2f' % y, ha='center', va= 'top') plt.xlim(-.5,n), plt.xticks([]) plt.ylim(-1.25,+1.25), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/bar_ex.png', dpi=48) plt.show()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ax = plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95], polar=True) N = 20 theta = np.arange(0.0, 2*np.pi, 2*np.pi/N) radii = 10*np.random.rand(N) width = np.pi/4*np.random.rand(N) bars = plt.bar(theta, radii, width=width, bottom=0.0) for r,bar in zip(radii, bars): bar.set_facecolor( plt.cm.jet(r/10.)) bar.set_alpha(0.5) ax.set_xticklabels([]) ax.set_yticklabels([]) # savefig('../figures/polar_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
hist()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 mu,sigma=100,15 x=mu+sigma*np.random.randn(10000) n,bins,patches=plt.hist(x,50,normed=1,facecolor='g',alpha=0.75) plt.xlabel('Smarts') plt.ylabel('Probability') plt.title('Histogram of IQ') plt.text(60,.025, r'$\mu=100,\ \sigma=15$') plt.axis([40,160,0,0.03]) plt.grid(True)
pie()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 20 Z = np.ones(n) Z[-1] *= 2 plt.axes([0.025, 0.025, 0.95, 0.95]) plt.pie(Z, explode=Z*.05, colors=['%f' % (i/float(n)) for i in range(n)], wedgeprops={"linewidth": 1, "edgecolor": "black"}) plt.gca().set_aspect('equal') plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/pie_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
scatter()
【数字的可视化:python 画图之散点图 sactter 函数详解】
s:点大小。
marker:点形态。
c:颜色序列。可以是单个颜色、向量、cmap数字,RGB位矩阵
cmap:自行设置颜色映射。
norm:亮度。[0, 1]。
vmin,vmax:同 norm。当 norm 不存在时生效。
linewidths:点缘宽度。
edgecolors:点缘颜色。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 1024 X = np.random.normal(0,1,n) Y = np.random.normal(0,1,n) T = np.arctan2(Y,X) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) plt.scatter(X,Y, s=75, c=T, alpha=.5) plt.xlim(-1.5,1.5), plt.xticks([]) plt.ylim(-1.5,1.5), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/scatter_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
imshow()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def f(x,y): return (1-x/2+x**5+y**3)*np.exp(-x**2-y**2) n = 10 x = np.linspace(-3,3,3.5*n) y = np.linspace(-3,3,3.0*n) X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) Z = f(X,Y) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) plt.imshow(Z,interpolation='bicubic', cmap='bone', origin='lower') plt.colorbar(shrink=.92) plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/imshow_ex.png', dpi=48) plt.show()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) X = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25) Y = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25) X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2) Z = np.sin(R) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=plt.cm.hot) ax.contourf(X, Y, Z, zdir='z', offset=-2, cmap=plt.cm.hot) ax.set_zlim(-2,2) # savefig('../figures/plot3d_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
contourf()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def f(x,y): return (1-x/2+x**5+y**3)*np.exp(-x**2-y**2) n = 256 x = np.linspace(-3,3,n) y = np.linspace(-3,3,n) X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) plt.contourf(X, Y, f(X,Y), 8, alpha=.75, cmap=plt.cm.hot) C = plt.contour(X, Y, f(X,Y), 8, colors='black', linewidth=.5) plt.clabel(C, inline=1, fontsize=10) plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/contour_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
quiver()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 8 X,Y = np.mgrid[0:n,0:n] T = np.arctan2(Y-n/2.0, X-n/2.0) R = 10+np.sqrt((Y-n/2.0)**2+(X-n/2.0)**2) U,V = R*np.cos(T), R*np.sin(T) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) plt.quiver(X,Y,U,V,R, alpha=.5) plt.quiver(X,Y,U,V, edgecolor='k', facecolor='None', linewidth=.5) plt.xlim(-1,n), plt.xticks([]) plt.ylim(-1,n), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/quiver_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
grid()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ax = plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) ax.set_xlim(0,4) ax.set_ylim(0,3) ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.MultipleLocator(1.0)) ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(plt.MultipleLocator(0.1)) ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.MultipleLocator(1.0)) ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(plt.MultipleLocator(0.1)) ax.grid(which='major', axis='x', linewidth=0.75, linestyle='-', color='0.75') ax.grid(which='minor', axis='x', linewidth=0.25, linestyle='-', color='0.75') ax.grid(which='major', axis='y', linewidth=0.75, linestyle='-', color='0.75') ax.grid(which='minor', axis='y', linewidth=0.25, linestyle='-', color='0.75') ax.set_xticklabels([]) ax.set_yticklabels([]) # savefig('../figures/grid_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure() fig.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.025, left=0.025, top = 0.975, right=0.975) plt.subplot(2,1,1) plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) plt.subplot(2,3,4) plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) plt.subplot(2,3,5) plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) plt.subplot(2,3,6) plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # plt.savefig('../figures/multiplot_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
text()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt eqs = [] eqs.append((r"$W^{3\beta}_{\delta_1 \rho_1 \sigma_2} = U^{3\beta}_{\delta_1 \rho_1} + \frac{1}{8 \pi 2} \int^{\alpha_2}_{\alpha_2} d \alpha^\prime_2 \left[\frac{ U^{2\beta}_{\delta_1 \rho_1} - \alpha^\prime_2U^{1\beta}_{\rho_1 \sigma_2} }{U^{0\beta}_{\rho_1 \sigma_2}}\right]$")) eqs.append((r"$\frac{d\rho}{d t} + \rho \vec{v}\cdot\nabla\vec{v} = -\nabla p + \mu\nabla^2 \vec{v} + \rho \vec{g}$")) eqs.append((r"$\int_{-\infty}^\infty e^{-x^2}dx=\sqrt{\pi}$")) eqs.append((r"$E = mc^2 = \sqrt{{m_0}^2c^4 + p^2c^2}$")) eqs.append((r"$F_G = G\frac{m_1m_2}{r^2}$")) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) for i in range(24): index = np.random.randint(0,len(eqs)) eq = eqs[index] size = np.random.uniform(12,32) x,y = np.random.uniform(0,1,2) alpha = np.random.uniform(0.25,.75) plt.text(x, y, eq, ha='center', va='center', color="#11557c", alpha=alpha, transform=plt.gca().transAxes, fontsize=size, clip_on=True) plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/text_ex.png',dpi=48) plt.show()
参考资料:
Example gallery — seaborn 0.9.0 documentation
Seaborn 和 Matplotlib 数据可视化 - 简书
Seaborn 要求原始数据的输入类型为 pandas 的 Dataframe 或 Numpy 数组,画图函数一般为如下形式sns.图名(x='X轴 列名', y='Y轴 列名', data=原始数据df对象)sns.图名(x='X轴 列名', y='Y轴 列名', hue='分组绘图参数', data=原始数据df对象)sns.图名(x=np.array, y=np.array[, ...]) > > hue 的意思是 variable in data to map plot aspects to different colors。
seaborn: statistical data visualization — seaborn 0.9.0 documentation
seaborn 详解
Seaborn 在底层将matplotlib 参数分成了两个独立的组。第一组设定了美学风格 ,第二组则是不同的数据元素 ,这样就可以很容易地添加到代码当中了。
Seaborn(sns) 官方文档学习笔记(第二章斑驳陆离的调色板) - 知乎
python3.x-seaborn.heatmap 随笔
Seaborn相当于高级绘图。(Matplotlib则为基础)
GUI设置set()
see in set()
style=:(背景,set_styleaxes_style()
1 2 3 4 5 darkgrid 黑色网格(默认) whitegrid 白色网格 dark 黑色背景 white 白色背景 ticks 加上刻度的白色背景
context=:(线条粗细,依次变粗,set_contextplotting_context()
1 2 3 4 paper notebook talk poster
palette=:(数据颜色,set_paletteset_color_codescolor_palette()
1 2 3 4 5 6 deep muted pastel bright dark colorblind
Choosing color palettes
调色板函数:palplot()
font=:(字形)
font_scale:(字体)
sns.set()空调用 可以重置 风格参数。
color_palette()
see in color_palette()
subplots()|subplot()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns import numpy as np import pandas as pd f, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=2, figsize=(8, 6)) X = np.arange(0.01, 10, 0.01) Zeros = np.where(X is not 0,X,0) ax[0, 0].plot(X, 1/(1+np.exp(-X))) ax[0, 0].set_title("Logistic") ax[0, 1].plot(X, np.maximum(Zeros,X)) ax[0, 1].set_title("ReLU") ax[1, 0].plot(X, np.exp(X)) ax[1, 0].set_title("Exp") ax[1, 1].plot(X, np.sin(X)) ax[1, 1].set_title("Sin") plt.show()
1 2 3 4 5 6 plt.figure(figsize=(3, 3)) # 全图分成2x2,分别占用第1、2个,即第一行第二列的子图 plt.subplot(221) plt.subplot(222) # 全图分成2x1,占用第2个,即第二行 plt.subplot(212)
barplot()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns import numpy as np import pandas as pd X = np.arange(8) y = np.array([1, 4, 2, 3, 3, 5, 6, 3]) df = pd.DataFrame({"X":X, "y":y}) sns.barplot("X", "y", palette="RdBu_r", data=df) # or下面这种形式,但需要自行设置Xy轴的 label # sns.barplot(X, y, palette="RdBu_r") plt.show()
seaborn.barplot — seaborn 0.9.0 documentation
distplot()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 mu,sigma=100,15 x=mu+sigma*np.random.randn(10000) sns.set_color_codes() plt.xlabel('Smarts') plt.ylabel('Probability') plt.title('Histogram of IQ') plt.text(60,.025, r'$\mu=100,\ \sigma=15$') sns.distplot(x, color="y")
countplot()
plotting value_counts() in seaborn barplot - Stack Overflow
seaborn.countplot — seaborn 0.9.0 documentation
1 2 3 4 sns.set(style="darkgrid") titanic = sns.load_dataset("titanic") sns.countplot(x="who", data=titanic)
hue=‘something’1 2 f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6)) sns.countplot(x="who", hue="class", data=titanic, ax=ax)
Seaborn 包画出好看的分布图(Python) - 来自西北的杨柳 - CSDN 博客
violinplot()
seaborn.violinplot
1 2 3 4 5 6 sns.set(style="whitegrid", palette="pastel", color_codes=True) tips = sns.load_dataset("tips") sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips) sns.despine(left=True)
hue=‘something’1 2 3 sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="sex", data=tips, split=True, inner="quart", palette={"Male": "b", "Female": "y"}) sns.despine(left=True)
boxplots()1 2 3 4 5 6 sns.set(style="whitegrid", palette="pastel", color_codes=True) # Load the example tips dataset tips = sns.load_dataset("tips") sns.boxplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, palette="PRGn") sns.despine(offset=10, trim=True) # 设置边框的风格
hue=‘something’1 2 sns.boxplot(x="sex", y="total_bill", hue="day", data=tips, palette="PRGn") sns.despine(offset=10, trim=True)
scatterplot()聚类是无监督,散类是有监督。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 sns.set() # Load the example iris dataset planets = sns.load_dataset("planets") cmap = sns.cubehelix_palette(rot=-.2, as_cmap=True) ax = sns.scatterplot(x="distance", y="orbital_period", hue="year", size="mass", palette=cmap, sizes=(10, 200), data=planets)
lmplot()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 sns.set(style="ticks") # Load the example dataset for Anscombe's quartet df = sns.load_dataset("anscombe") # Show the results of a linear regression within each dataset sns.lmplot(x="x", y="y", col="dataset", hue="dataset", data=df, col_wrap=2, ci=None, palette="muted", height=4, scatter_kws={"s": 50, "alpha": 1})
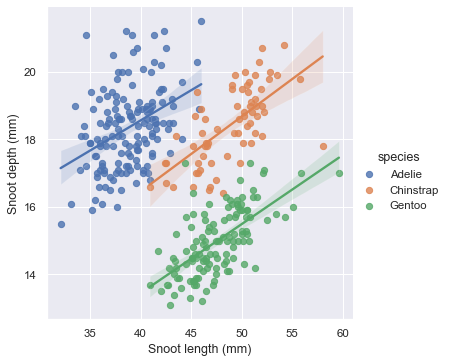
hue='something’1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 sns.set() # Load the iris dataset iris = sns.load_dataset("iris") # Plot sepal with as a function of sepal_length across days g = sns.lmplot(x="sepal_length", y="sepal_width", hue="species", truncate=True, height=5, data=iris) # Use more informative axis labels than are provided by default g.set_axis_labels("Sepal length (mm)", "Sepal width (mm)")
order=21 2 3 4 sns.set(color_codes=True) anscombe = sns.load_dataset("anscombe") sns.lmplot(x="x", y="y", data=anscombe.query("dataset == 'II'"), order=2, ci=None, scatter_kws={"s": 80})
还可设置:robust=True鲁棒性,logistic=True用逻辑函数拟合,
jointplot()
Seaborn-04-Jointplot 两变量图 - 简书
1 2 3 4 5 sns.set(style="darkgrid") tips = sns.load_dataset("tips") g = sns.jointplot("total_bill", "tip", data=tips, kind="reg", xlim=(0, 60), ylim=(0, 12), color="m", height=7)
kind=kde:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 sns.set(style="white") # Generate a random correlated bivariate dataset rs = np.random.RandomState(5) mean = [0, 0] cov = [(1, .5), (.5, 1)] x1, x2 = rs.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 500).T x1 = pd.Series(x1, ) x2 = pd.Series(x2, ) # Show the joint distribution using kernel density estimation g = sns.jointplot(x1, x2, kind="kde", height=7, space=0)
residplot()对比与一阶拟合曲线的残差。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 sns.set(style="whitegrid") # Make an example dataset with y ~ x rs = np.random.RandomState(7) x = rs.normal(2, 1, 75) y = 2 + 1.5 \* x + rs.normal(0, 2, 75) # Plot the residuals after fitting a linear model sns.residplot(x, y, lowess=True, color="g")
pairplot()1 2 3 4 sns.set(style="ticks") df = sns.load_dataset("iris") sns.pairplot(df, hue="species")
swarmplot()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 sns.set(style="whitegrid", palette="muted") # Load the example iris dataset iris = sns.load_dataset("iris") # "Melt" the dataset to "long-form" or "tidy" representation iris = pd.melt(iris, "species", var\_) # Draw a categorical scatterplot to show each observation sns.swarmplot(x="measurement", y="value", hue="species", palette=["r", "c", "y"], data=iris)
heatmap()
seaborn.heatmap
10 Heatmaps 10 Python Libraries
相关系数矩阵与热力图 heatmap(Python 高级可视化库 seaborn)
Python 可视化:Seaborn 库热力图使用进阶 - 简书
heatmap需要传入一个浮点数矩阵 。如果NaN则会绘制为空白格。
1 2 3 df = sns.load_dataset("iris") sns.heatmap(df.corr(), square=True)
1 2 3 4 5 6 df = sns.load_dataset("iris") colormap = plt.cm.viridis plt.figure(figsize=(6,6)) # 根据需要自行设置大小(也可省略) plt.title('Pearson Correlation of Features', y=1.05, size=15) # 加标题 sns.heatmap(df.corr(),linewidths=0.1,vmax=1.0, square=True, cmap=colormap, linecolor='white', annot=True)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 flights_long = sns.load_dataset("flights") flights = flights_long.pivot("month", "year", "passengers") # 绘制x-y-z的热力图,比如 年-月-销量 的热力图 f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9, 6)) #绘制热力图,将数值写到热力图上 sns.heatmap(flights, annot=True, fmt="d", ax=ax) #设置坐标字体方向 label_y = ax.get_yticklabels() plt.setp(label_y, rotation=360, horizontalalignment='right') label_x = ax.get_xticklabels() plt.setp(label_x, rotation=45, horizontalalignment='right')
kdeplot()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 sns.set(style="darkgrid") iris = sns.load_dataset("iris") # Subset the iris dataset by species setosa = iris.query("species == 'setosa'") virginica = iris.query("species == 'virginica'") # Set up the figure f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8)) ax.set_aspect("equal") # Draw the two density plots ax = sns.kdeplot(setosa.sepal_width, setosa.sepal_length, cmap="Reds", shade=True, shade_lowest=False) ax = sns.kdeplot(virginica.sepal_width, virginica.sepal_length, cmap="Blues", shade=True, shade_lowest=False) # Add labels to the plot red = sns.color_palette("Reds")[-2] blue = sns.color_palette("Blues")[-2] ax.text(2.5, 8.2, "virginica", size=16, color=blue) ax.text(3.8, 4.5, "setosa", size=16, color=red)
clustermap()
seaborn.clustermap
二维用热聚类,高维用聚类散图。
method=:Here 。聚类方法【距离度量】。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 complete #最远邻,默认方法 single #最近邻,Voor Hees Algorithm average #平均距离,和complete效果几乎相同,UPGMA algorithm weighted #与single相似,非平凡点相对更密集。逐步距离,WPGMA #以下仅适用欧式空间 centroid #中心度量 median #类似centroid,WPGMC algorithm ward #incremental algorithm
1 2 3 4 5 sns.set(color_codes=True) df = sns.load_dataset("iris") species = df.pop("species") sns.clustermap(df)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 # Load the brain networks example dataset df = sns.load_dataset("brain_networks", header=[0, 1, 2], index_col=0) # Select a subset of the networks used_networks = [1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 12, 13, 17] used_columns = (df.columns.get_level_values("network") .astype(int) .isin(used_networks)) df = df.loc[:, used_columns] # Create a categorical palette to identify the networks network_pal = sns.husl_palette(8, s=.45) network_lut = dict(zip(map(str, used_networks), network_pal)) # Convert the palette to vectors that will be drawn on the side of the matrix networks = df.columns.get_level_values("network") network_colors = pd.Series(networks, index=df.columns).map(network_lut) # Draw the full plot sns.clustermap(df.corr(), center=0, cmap="vlag", row_colors=network_colors, col_colors=network_colors, linewidths=.75, figsize=(13, 13))
PairGrid()大杀器。orz
seaborn.PairGrid — seaborn 0.9.0 documentation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 sns.set(style="white") df = sns.load_dataset("iris") g = sns.PairGrid(df, diag_sharey=False) g.map_lower(sns.kdeplot) #指定下三角 g.map_upper(sns.scatterplot) #指定上三角 g.map_diag(sns.kdeplot, lw=3) #
指定hue='species':
More:Seaborn(sns) 官方文档学习笔记(第六章 绘制数据网格)
lineplot()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 sns.set(style="whitegrid") rs = np.random.RandomState(365) values = rs.randn(365, 4).cumsum(axis=0) dates = pd.date_range("1 1 2016", periods=365, freq="D") data = pd.DataFrame(values, dates, columns=["A", "B", "C", "D"]) data = data.rolling(7).mean() sns.lineplot(data=data, palette="tab10", linewidth=2.5)
hue='something'1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 sns.set(style="darkgrid") # Load an example dataset with long-form data fmri = sns.load_dataset("fmri") # Plot the responses for different events and regions sns.lineplot(x="timepoint", y="signal", hue="region",, data=fmri)
FacetGrid()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 sns.set() # Generate an example radial datast r = np.linspace(0, 10, num=100) df = pd.DataFrame({'r': r, 'slow': r, 'medium': 2 _ r, 'fast': 4 _ r}) # Convert the dataframe to long-form or "tidy" format df = pd.melt(df, id_vars=['r'], var_name='speed', value_name='theta') # Set up a grid of axes with a polar projection g = sns.FacetGrid(df, col="speed", hue="speed", subplot_kws=dict(projection='polar'), height=4.5, sharex=False, sharey=False, despine=False) # Draw a scatterplot onto each axes in the grid g.map(sns.scatterplot, "theta", "r")
animation.FuncAnimation()1 from matplotlib import animation
Redrawing Seaborn Figures for Animations - Stack Overflow
matplotlib 秘技:让可视化图形动起来
Animation 动画 莫烦 python
animation — Matplotlib 3.0.2 documentation
Save Matplotlib Animations as GIFs Embedding Matplotlib Animations in Jupyter Notebooks
python matplotlib 绘制 gif 动图以及保存
一步一步教你用 Matplotlib 保存 GIF 动图
由于这一节跟时间序列有关,所以放到这里。
Pre :conda install -c conda-forge ffmpeg
Pre2 :pip install --no-cache-dir -I pillow
Pre3:安装imagemagick(Here )
~忽然觉得有些多此一举,如果 mp4 也能 show,干嘛非得转成 gif?强迫症 orz~。
Welcome to Bokeh
可视化篇:流式数据监控(python)
用 Python 和 MoviePy 将数据动态可视化
『数据可视化』基于 Python 的数据可视化工具
https://plot.ly/python/
https://github.com/andrea-cuttone/geoplotlib
参考资料:
scipy.org
Scipy_Ref
Scipy-Lecture-Notes ,中文版
[Scipy 中文文档] 一篇文章快速入门 Scipy 教程
科学计算。包括统计, 优化, 整合, 线性代数模块, 傅里叶变换, 信号和图像处理, 常微分方程求解器等等。
(待续)
参考资料:
SymPy ,SymPy Tutorial — SymPy 1.3 documentation
3.2 Sympy:Python 中的符号数学 | SciPy Lecture Notes 中文版
教程— SymPy 0.7.2-git documentation
符号代数。